Noise Attenuation & Sensor Protection
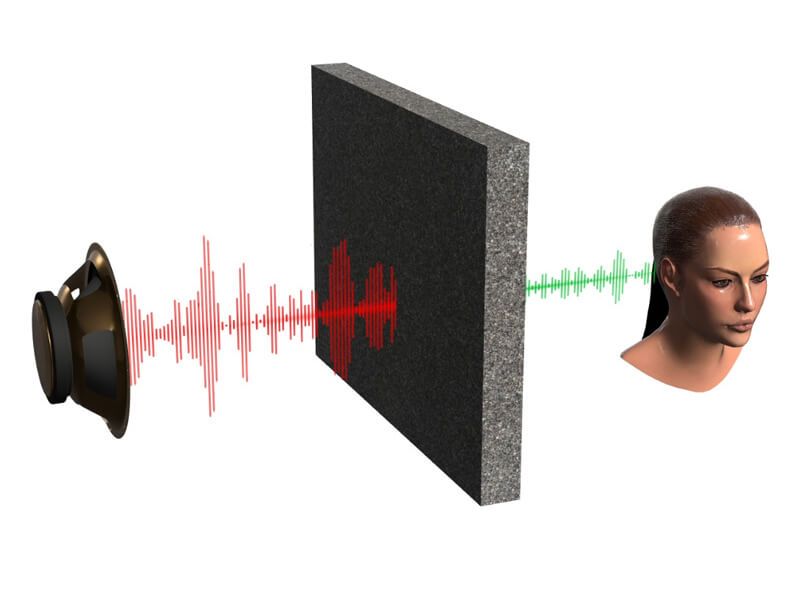
Porous elements are permeable to sound and can be used in shielded electrical panels, to prevent combustible gases from penetrating the panel, but allowing alarm sounds to be heard. Porous media also physically protect sensors, such as those that measure temperature. The porous material allows the sensor to operate, protecting it against interference from the environment. The animation shows the sound being attenuated by the porous medium. The ear can be considered a sensor, which can be protected by the sintered component.
Porous elements are permeable to sound and can be used in shielded electrical panels or as noise attenuators. Porous media also physically protect sensors, for temperature or gases, allowing a good measurement without contaminating the sensors.
-
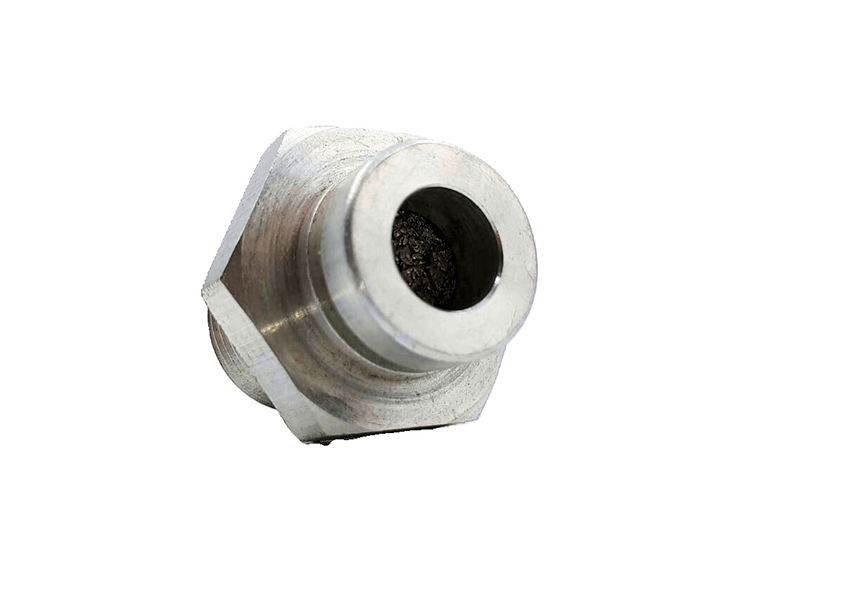

Sensor protection
The figure shows a metal flange (solid) with a central hole, where a porous disc is embedded. In this way, it protects a sensor, avoiding any contact with the external environment other than through the porous disc. This way, this sensor is protected from external agents that could eventually damage it. -
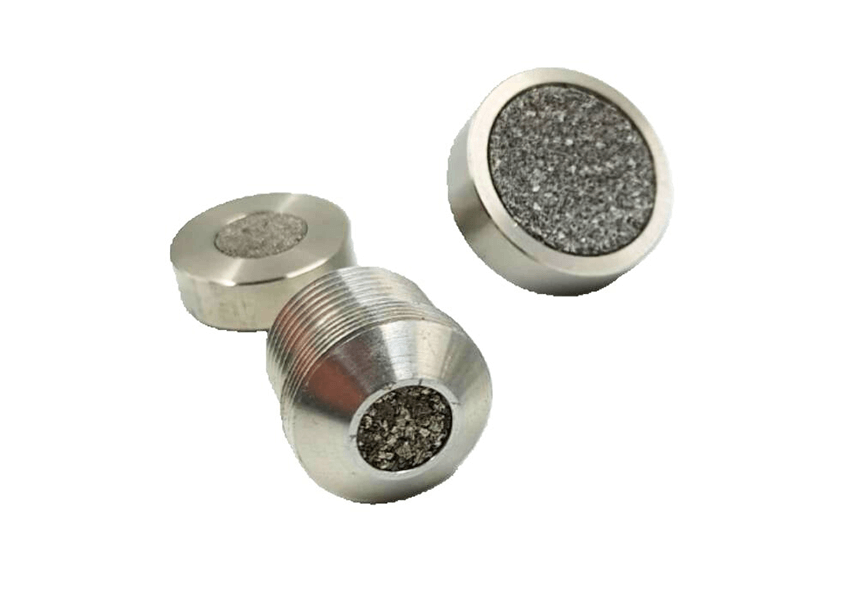

Explosion protection
Devices such as those are used in electrical panels, where protection against the entry of explosive gases is necessary. This way, sounds generated by this panel can be heard externally, without there being any danger of explosion. -
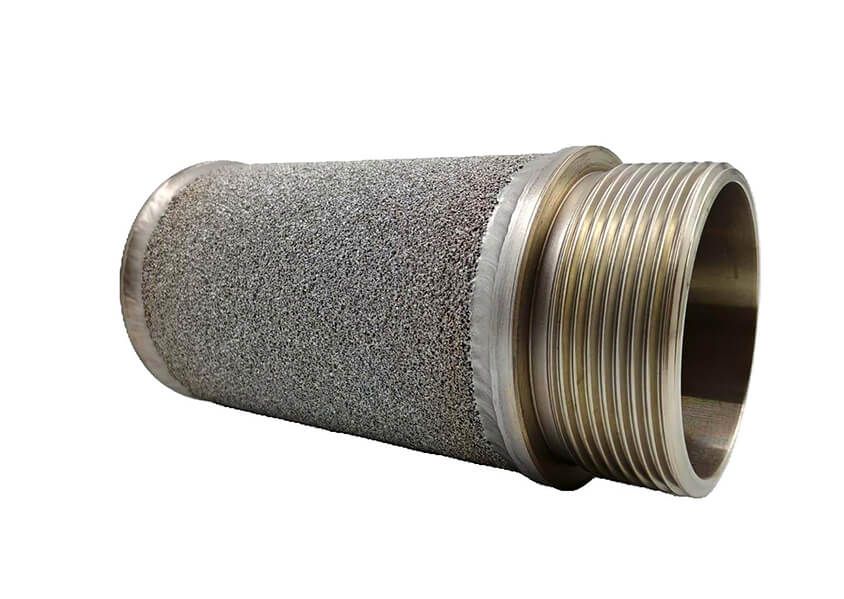

Noise attenuation
This device is used, for example, in equipment where gas may be discharged, generating strong noise, causing it to be significantly attenuated.