Filtration & Retention
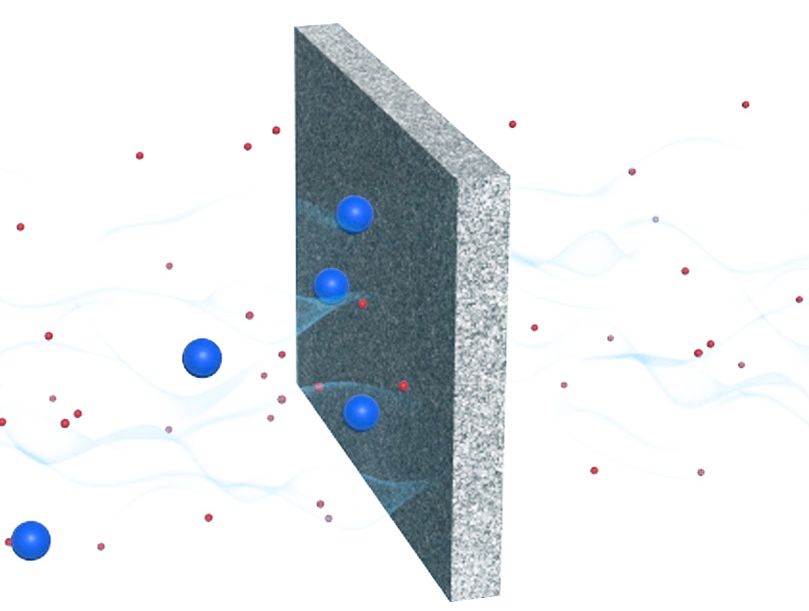
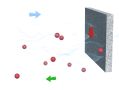
In a process that involves filtration, the sintered porous element establishes a physical barrier, allowing the passage of the fluid, liquid or gas. However, it retains the passage of particles that are larger than the filter opening (pore size). This opening can be adjusted according to the needs of each application. In the following animation, the fluid goes from left to right, and the filter opening, in this example 5 microns, is smaller than the diameter of the red particles, which are retained, unlike the blue ones.
The sintered porous element acts as a physical barrier, allowing the passage of fluid (liquid or gas), without the passage of particles. The size of the particles retained is defined by the filter opening.
-
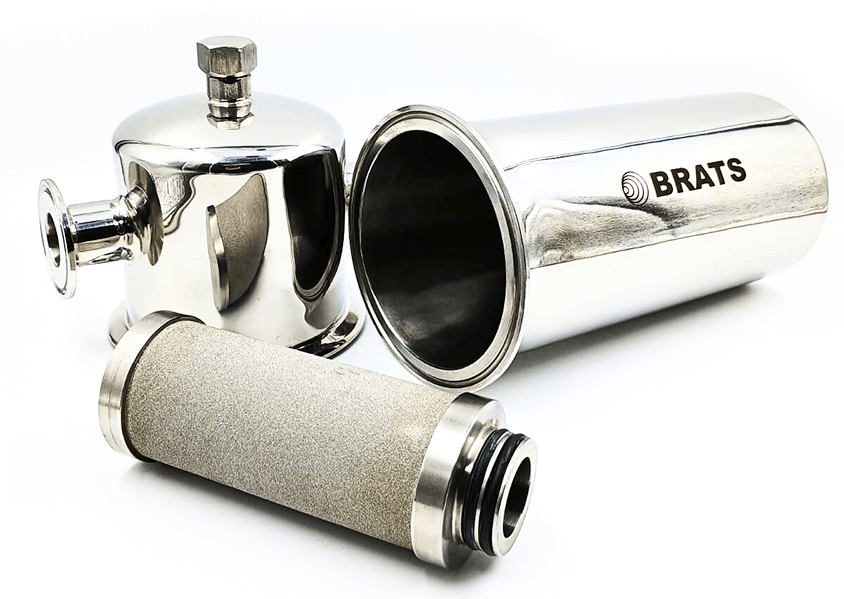

Sanitary steam
This is a filtration system widely used in dairy products (sanitary steam), with the aim of retaining particles that can be dragged from the boiler (steam generation), causing possible contamination in the final product. -
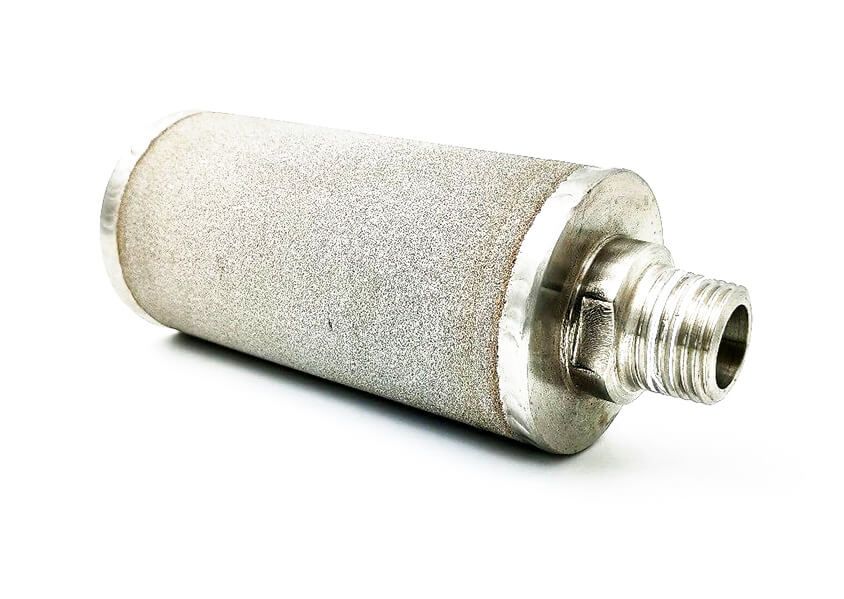

General purpose filter element
This is an example of a general purpose filter element, used in the filtration of gases and liquids, with the ability to retain particles of specific sizes, according to their porosity (filter opening), which is defined in the manufacturing process. -
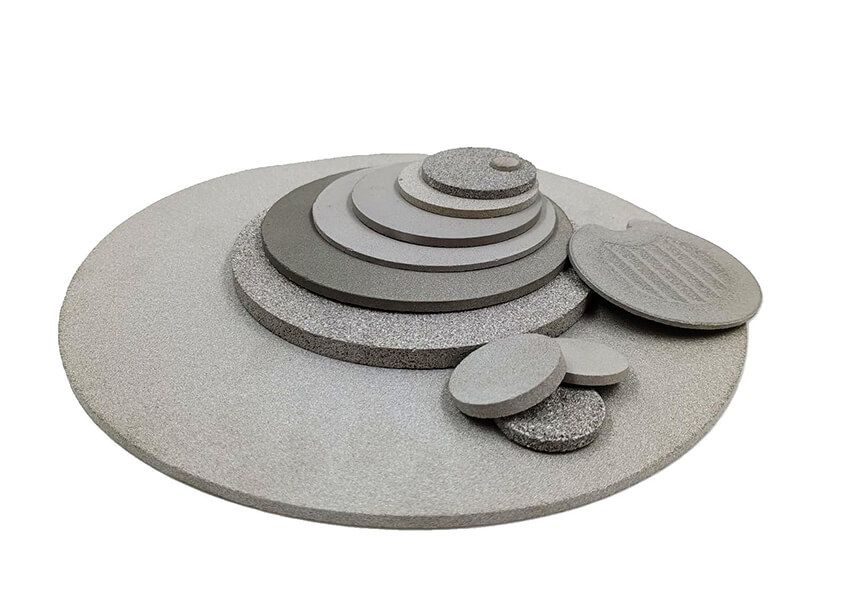

Various porous elements for filtration
In the photo we can identify several discs that can be used both as a filter element and as a substrate for porous membranes for filtration. There is also a disc with a “wavy” surface that is used in oil filtration.